The energy levels of the harmonic oscillator are
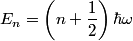 where 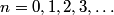 . So, the difference in energy between adjacent levels is always . So, the difference in energy between adjacent levels is always 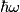 . So I is correct. . So I is correct. The potential energy is 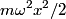 which is quadratic, not linear, in which is quadratic, not linear, in  , so II is incorrect. , so II is incorrect. The ground-state corresponds to 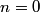 , and it has energy , and it has energy 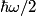 . This is equal to the kinetic energy plus the potential energy. By the virial theorem, . This is equal to the kinetic energy plus the potential energy. By the virial theorem, 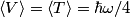 for this state, so the kinetic energy is not zero, and III is incorrect. for this state, so the kinetic energy is not zero, and III is incorrect. The wavefunction of the ground state of the harmonic oscillator is  where  and and 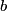 are positive constants. So, there is a nonzero probability for the particle to be found at any are positive constants. So, there is a nonzero probability for the particle to be found at any 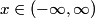 . So, IV is correct. . So, IV is correct. So, answer (C) is correct. |